Worksheet - Magnetic Effects of Electric Current
Magnetic Effects of Electric Current - Solved Worksheet
Recall
Magnetic Field Due to a Current Carrying Conductor
Right Hand Thumb Rule
Properties of Magnetic Field:
- The magnitude; of magnetic field increases with increase in electric current and decreases with decrease in electric current.
- The magnitude of magnetic field; produced by electric current; decreases with increase in distance and vice-versa. The size of concentric circles of magnetic field lines increases with distance from the conductor, which shows that magnetic field decreases with distance.
- Magnetic field lines are always parallel to each other.
- No two field lines cross each other.
Solenoids
Earth.
Force on a Current carrying Conductor in a Magnetic Field
Fuse
Short-circuit
Overloading
Earthing
Check your Concepts:
1. The most suitable material for making the core of an electromagnet is:
a) Steel
b) Iron
c) Soft iron
d) Aluminum
Answer: c
2. When a straight conductor is carrying current:
a) There are circular magnetic field lines around it
b) There are magnetic field lines parallel to the conductor
c) There are no magnetic field lines
d) None of the above
Answer: a
3.Two magnetic field lines:
a) Intersect at the neutral point
b) Never intersect each other
c) Intersect near north-pole or South Pole
d) Intersect at the midpoint of the magnet
Answer: c
4. A student learns that magnetic field strength around a bar magnet is different at every point.
Which diagram shows the correct magnetic field lines around a bar magnet?
Answer: c
5. The magnetic field inside a long straight solenoid carrying current:
a) Is zero?
b) Decrease as we move towards its end
c) Is the same at all points?
d) Increase as we move towards its end
Answer: c
6. A student places some iron filings around a magnet. The iron fillings arrange themselves as shown in the image.
The student labeled four different regions around the magnet. Where would the magnetic field be the strongest?
(a) P
(b) Q
(c) R
(d) S
Answer: c
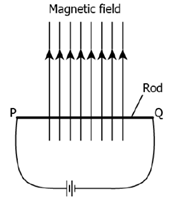
7. A metal rod PQ is placed in the magnetic field. The ends of the rod are connected to a battery using wires.
Where will the rod move?
(a) Upward
(b) Downwards
(c) Into the field
(d) Out of the field
Answer: d
8. A soft iron bar is introduced inside a current-carrying solenoid. The magnetic field inside a solenoid:
a) Decrease
b) Will increase
c) Will become zero
d) Will remain unaffected
Answer: b
9. Appliances that have a metal body are generally connected to the earthing wire. What is the reason to earth these wires?
(a) To prevent the excess current
(b) To prevent the leakage of current
(c) To provide extra current to the appliance
(d) To provide high resistance to the appliance
Answer: b
10. Which of the following correctly describes the magnetic field near a long straight wire?
a) The field consists of straight lines perpendicular to the wire
b) The field consists of straight lines parallel to the wire
c) The field consists of radial lines originating from the wire
d) The field consists of concentric circles centered on the wire
Answer: d
11. Magnetic effect of current was discovered by
(a) Oersted
(b) Faraday
(c) Bohr
(d) Ampere
Answer: a
12. The instrument that use to detect electric current in the circuit is known as
(a) Electric motor
(b) A.C generator
(c) Galvanometer
(d) None of the above
Answer: c
13. If the key in the given arrangement is taken out (the circuit is made open) and magnetic field lines are drawn over the horizontal plane ABCD, the lines are –
(a) Concentric circles
(b) Elliptical in shape
(c) Straight lines parallel to each other
(d) Concentric circles near the point O but of elliptical shapes as we go away from it
Answer: a
14. The most important safety method used for protecting home appliances from short circuiting or overloading is
(a) earthing
(b) use of fuse
(c) use of stabilizers
(d) use of electric meter
Answer: b
15. Switches are connected to –
(a) live wire.
(b) Neutral wire.
(c) Earth wire.
(d) Any one.
Answer: a
16. A circular loop placed in a plane perpendicular to the plane of paper carries a current when the key is ON. The current as seen from points A and B (in the plane and on the axis of the coil) is anticlockwise and clockwise respectively. The magnetic field lines point from B to A. The N-Pole of the resultant magnet is on the faces close to –
(a) A
(b) B
(c) A if the current is small, and B if the current is large
(d) B if the current is small, and A if the current is large
Answer: a
Actually, the magnetic fields emerge from North Pole of magnet, and go into the South Pole.
17. In the arrangement shown in the figure there are two coils on a non-conducting cylindrical rod. Initially the key is not inserted. Then the key is inserted and later removed. Then
(a) The deflection in the galvanometer remains zero throughout
(b) There is a momentary deflection in the galvanometer but it dies out shortly and there is no effect when the key is removed
(c) There are momentary galvanometer deflections that die out shortly, the deflections are in the same direction.
(d) There are momentary galvanometer deflections that die out shortly, the deflections are in the opposite direction.
Answer: a
There are momentary galvanometer deflections that die out shortly; the deflections are in opposite directions. When the key is inserted in the circuit of coil 1, there is a momentary increase of current. This change in current produces a change in the magnetic field. Since changing magnetic field induces a current, a momentary deflection is seen in the circuit of coil 2.
Similarly, on removing the key, the current becomes zero quickly, and there is a change in the current in coil 1. And, this current change induces a current in coil 2. But this time the deflection happens in the opposite direction.
18. The strength of magnetic field inside a long current carrying straight solenoids is –
(a) more at the ends than at the center
(b) minimum in the middle
(c) same at all points
(d) found to increase from one end to the other
Answer: c
The magnetic field lines inside a current carrying solenoid are parallel and equidistant which means the strength of magnetic field is uniform inside the solenoid i.e. same at all points.
19. Magnetic field lines
(a) have one direction at a point
(b) have no physical reality
(c) can be used to indicate the direction of the magnetic field of a point
(d) all the above
Answer: d
20. A current carrying wire in the neighborhood produces
(a) no field
(b) electric and magnetic fields
(c) Electric field only
(d) magnetic field only
Answer: b
 Reviewed by Syed Hafiz Choudhary
on
December 31, 2023
Rating:
Reviewed by Syed Hafiz Choudhary
on
December 31, 2023
Rating:










No comments: